The lateral performance of modular buildings
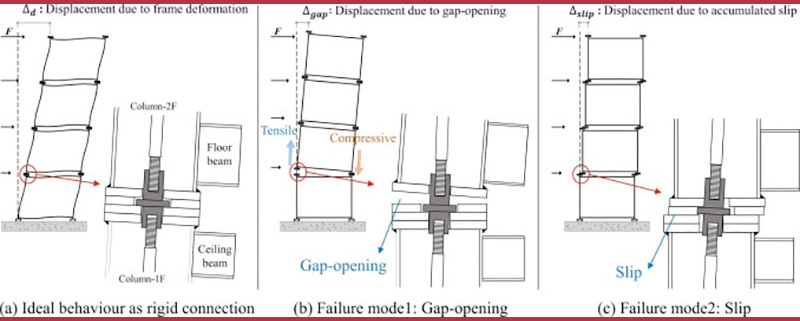
The global demand for multi-storey steel-framed modular buildings is rapidly increasing, driving the development of post-tensioned inter-module connections that enhance factory prefabrication and minimize site work for rapid construction. However, the lateral performance of modular buildings with these connections has been inadequately assessed due to the lack of 2D models capable of simulating key failure modes, such as gap-opening and slip. This study proposes a simplified 2D finite element (FE) connection model to simulate these failure modes and evaluates the lateral performance of mid-rise modular buildings using an innovative bolt-free post-tensioned inter-module connection, termed the ‘AJ connection.’ Designed for easy assembly and disassembly, it facilitates fast construction and reusability. First, the developed 2D model is validated against a 3D connection model calibrated to experimental results, then applied to mid-rise moment-resisting frames (MRFs) composed of modules to assess their performance under design wind and seismic loads. Compared to MRFs featuring welded connections, MRFs with AJ connections demonstrate nearly equivalent performance under wind loads, but slightly inferior performance under earthquake loads. Nevertheless, they demonstrate excellent seismic performance by exhibiting strong-column-weak-beam behaviour, satisfying most FEMA 365 performance objectives. Moreover, using identical cross-sections for floor and ceiling beams improves the lateral stiffness, strength, and ductility, while reducing the required preload for the AJ connections, compared to using beams of different sizes.
CLICK HERE TO DOWNLOAD THE FULL TECHNICAL REPORT
Source: Science Direct





Leave a Reply
Want to join the discussion?Feel free to contribute!